This article provides a concise overview of hydraulic control systems, their components, and maintenance, along with an explanation of how hydraulic fluid works. Proper understanding and care of these systems can ensure their reliable operation in various industrial applications.
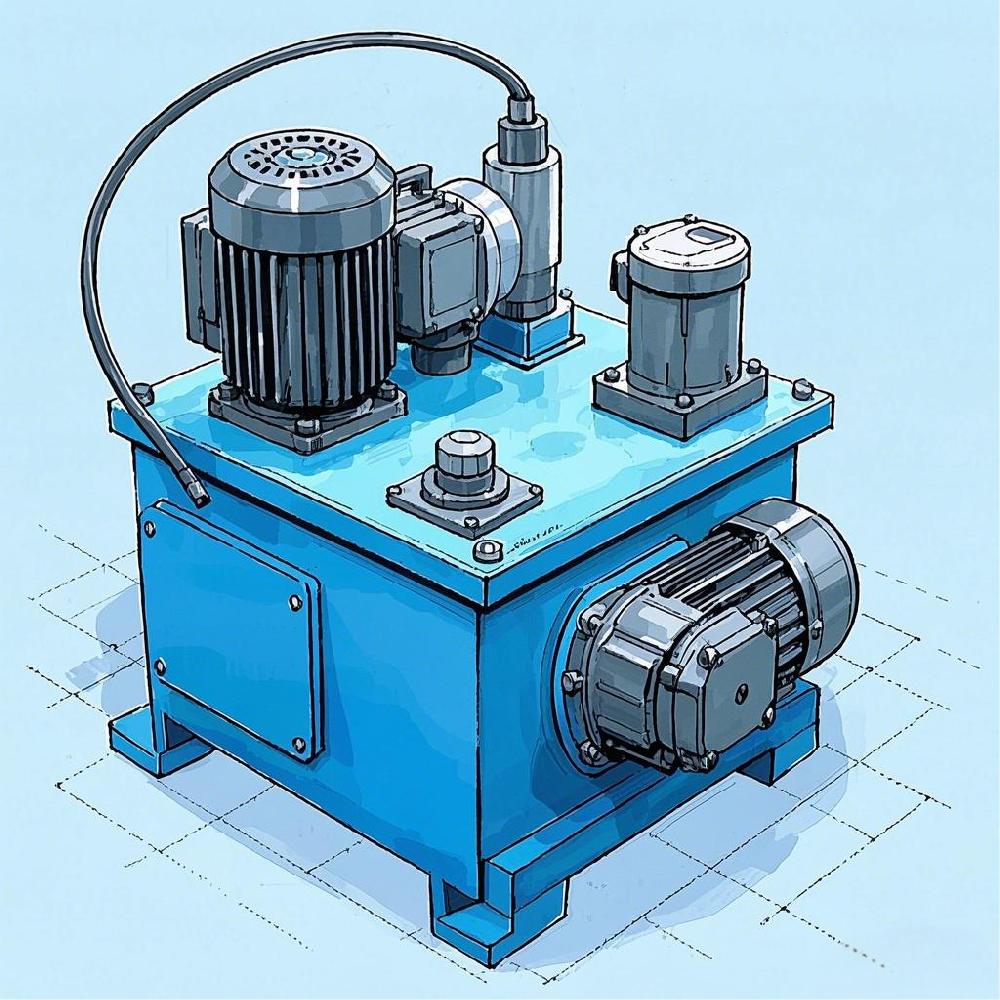
Hydraulic System Components
A hydraulic control system is composed of several key components that work together to transmit power and control movement. These include:
Power Elements: Hydraulic pumps convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, providing pressurized fluid to the system.
Actuating Elements: Hydraulic cylinders and motors convert hydraulic energy back into mechanical energy to perform work such as linear or rotary motion.
Control Elements: Valves regulate the direction, pressure, and flow rate of the hydraulic fluid, ensuring precise control of the system.
Auxiliary Elements: These include oil tanks, filters, pipes, and seals, which support the system's operation and maintenance.
How Hydraulic Fluid Works
Hydraulic fluid is the medium through which power is transmitted in a hydraulic system. It operates based on Pascal's law, which states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid. The hydraulic pump pressurizes the fluid, which then flows through the control valves to the hydraulic cylinders or motors. The pressurized fluid pushes the pistons in the cylinders or turns the motors, creating mechanical motion. The fluid also serves as a lubricant and coolant, helping to reduce wear and prevent overheating.
Maintenance of Hydraulic Systems
Proper maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of hydraulic systems:
Fluid Checks: Regularly inspect the hydraulic fluid level and quality. Contaminated or low fluid can cause damage to components.
Filter Replacement: Replace filters as recommended to prevent debris from entering the system.
Leak Inspection: Check for leaks in pipes and seals, and repair them promptly to avoid fluid loss and system failure.
Component Lubrication: Lubricate moving parts to reduce friction and wear.